
WikiIran exposes here thousands of confidential documents leaked recently online from the internal servers of Iran’s largest petrochemical company “The Persian Gulf Petrochemical Industry Commercial Company (PGPICC).” The information highlighted here expose how this company has been circumventing the international sanctions against Iran’s petrochemical industry.
Banks and Money Service Businesses (MSB) in the UAE and China are ignoring clear red flags of money laundering; providing financial services to a network of front companies controlled by Iranian counterparts. <u>Thus, despite Iran being a High-risk jurisdiction (under U.S Sanctions and on the FATF black list) and the</u> Even though the UAE is on the FATF (Financial action task force) grey list, their financial system should be more vigilant to such Trade Based Money Laundering typologies.
PGPICC is Iran's largest petrochemical exporter, with foreign customers worldwide. Based on PGPICC's leaked documents, WikiIran's team has managed to identify a network consisting of over 180 front companies Outside of Iran. There is another group of Third-party companies, representing the Customers in these concealed transactions. All the Third-party companies hold bank accounts in major foreign international banks such as ICBC, First Abu Dhabi Bank, and Sohar bank.
These bank accounts are used to conceal, and therefore enable these Sanctioned transactions for PGPICC’s petrochemicals export. Based on PGPICC's documents, These financial transactions have totaled over $10.5 Billion just in the past two years. All of these transactions are done using money laundering typologies such as forged documents, hiding the Ultimate beneficiary owner (UBO) and concealing the real destination of these payments.
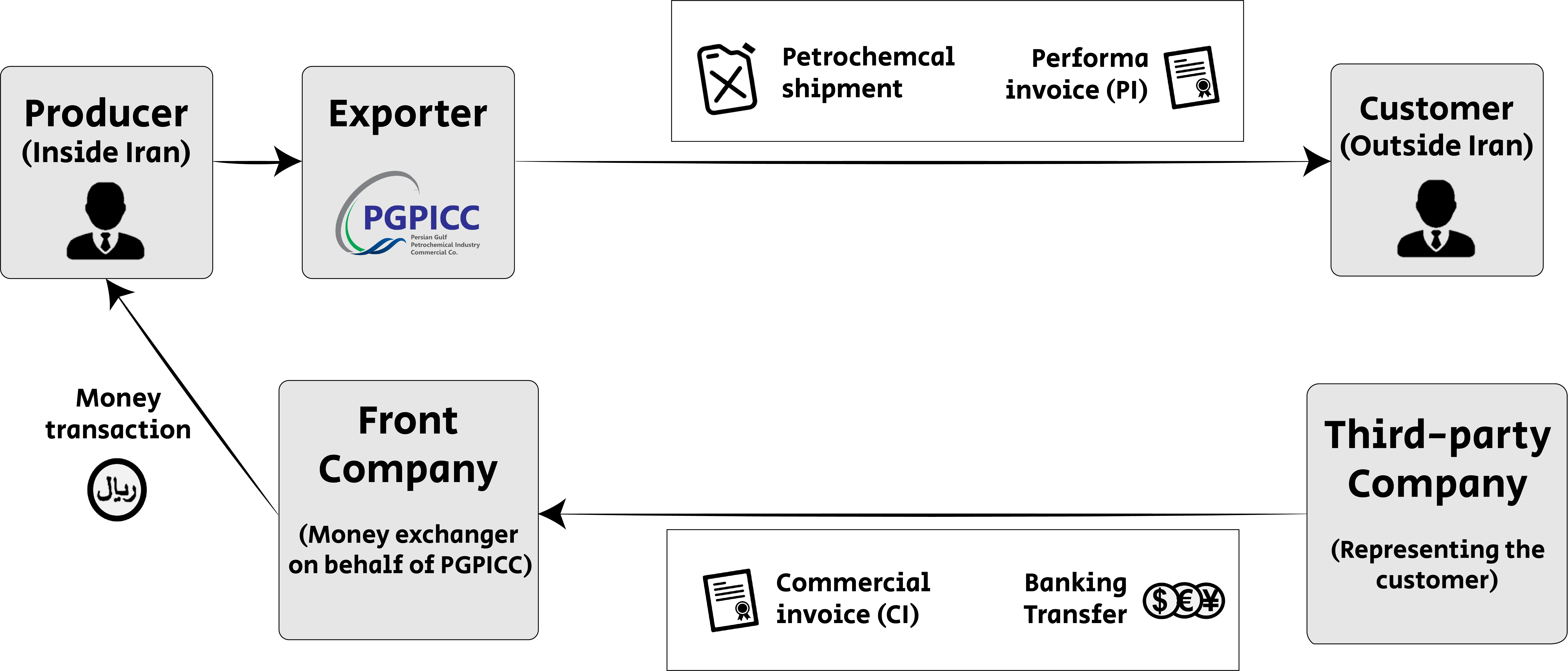
The process:
- A ‘legitimate’ Invoice issued between PGPICC and the customer on the PGPICC letterhead (as is pictured in the example).
- PGPICC issues a fraudulent invoice and use it to transfer the payment via the international banking system. The customer pays front company representing PGPICC (and operated by the money exchange house) in order to conceal the Iranian beneficiary. Often the customers are also using the service of third-party company. Sometimes payments are divided into multiple transactions, according to the terms in their contract.
- PGPICC ships the petrochemicals to the customer.
- The money held by the front company is sold by PGPICC to another Iranian company - in exchange for Rial (using the NIMA system).
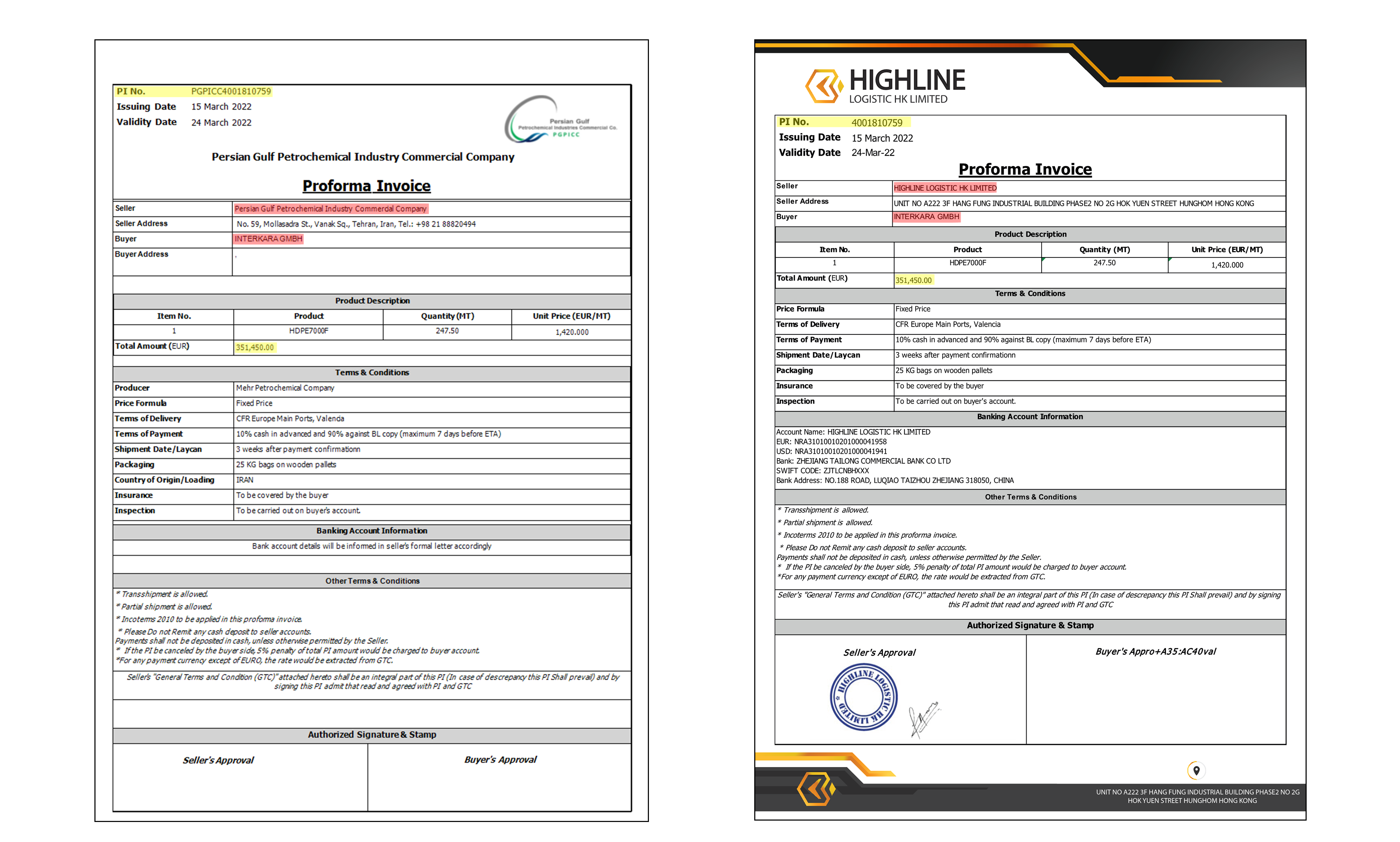
Here we have the 2 invoices: the authentic invoice (PI) issued by PGPICC to “INTERKARA GMBH”- the customer, and the Fraudulent Invoice (CI) issued by “HIGHLINE LOGISTIC HK LIMITED” - the front company representing PGPICC (owned by an Iranian money exchanger) to company “INTERKARAH GMBH” (the customer). Note how the contents of the documents match, the Invoice number, the Value, the BL date and even the format.
The system that PGPICC uses is identical to the system that was revealed in the Tahayyori database, and many of the front companies PGPICC are using, belong to Tahayyori.
About "Nima System":
The Nima System is Iran's central bank system for managing Iranian foreign currency. The system matches the Iranian importer's demands and the Iranian exporter's supply of foreign currency funds in varying fixed forex rates, and documents each foreign exchange conversion between the exporter and the importer. This system enables the Iranian central bank to improve its control over the Iranian foreign exchange market.